Recently I have been helping our marketing team with structured technical descriptions. While choosing topics, I realized how “AI” and “cloud computing” have become buzzwords. Most people only half understand them, but if you do not mention them you seem out of date. Since we are a SaaS provider, writing a cloud-computing explainer from that angle felt like a good direction.
Definition
Cloud computing is a technology that provides computing resources (such as servers, storage, databases, networks, and software) over the internet. It allows users to access and use these resources on demand without purchasing and maintaining local hardware or software. The core idea is to centralize computing resources and deliver them as services over the network.
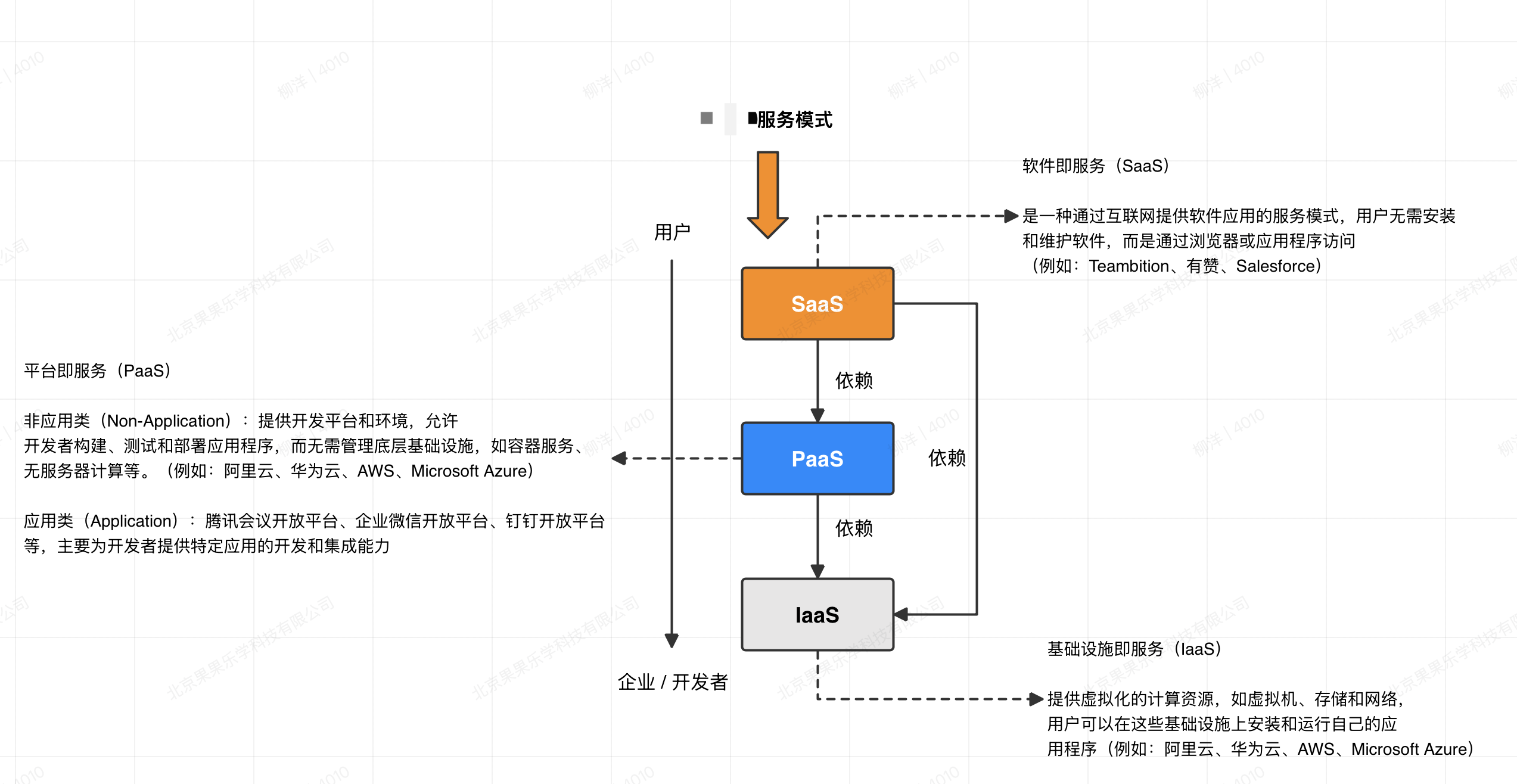
Service Models
Cloud computing has three service models, from bottom to top: IaaS -> PaaS -> SaaS.
Deployment Options
There are three common deployment options: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
[Our current deployment] Public Cloud
Provided by cloud vendors (e.g., Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure)
- Pros: cost-effective, scalable, flexible, high availability, and strong security (network and data security)
- Cons: relies on third-party providers; for some sensitive data (e.g., national security related), it may not be the best choice
Private Cloud
A cloud environment built for a single organization, hosted on-premise or in a third-party data center, with higher security (after a company and product reach a certain stage, this is typically chosen by key accounts with strict security requirements).
- Pros: stronger data security and privacy
- Cons: sacrifices some scalability and flexibility; high costs (servers and operations staff)
Hybrid Cloud
If you want the scalability and security of public cloud while keeping data on-premise to satisfy data residency laws, or to support compute closer to customers, hybrid cloud is a good fit.
- Pros: combines advantages of public and private cloud, easy to scale resources and storage while still accessing data and apps locally
- Cons: complex to manage; requires dedicated VPN or leased lines between public and private clouds; high demands on network speed and stability
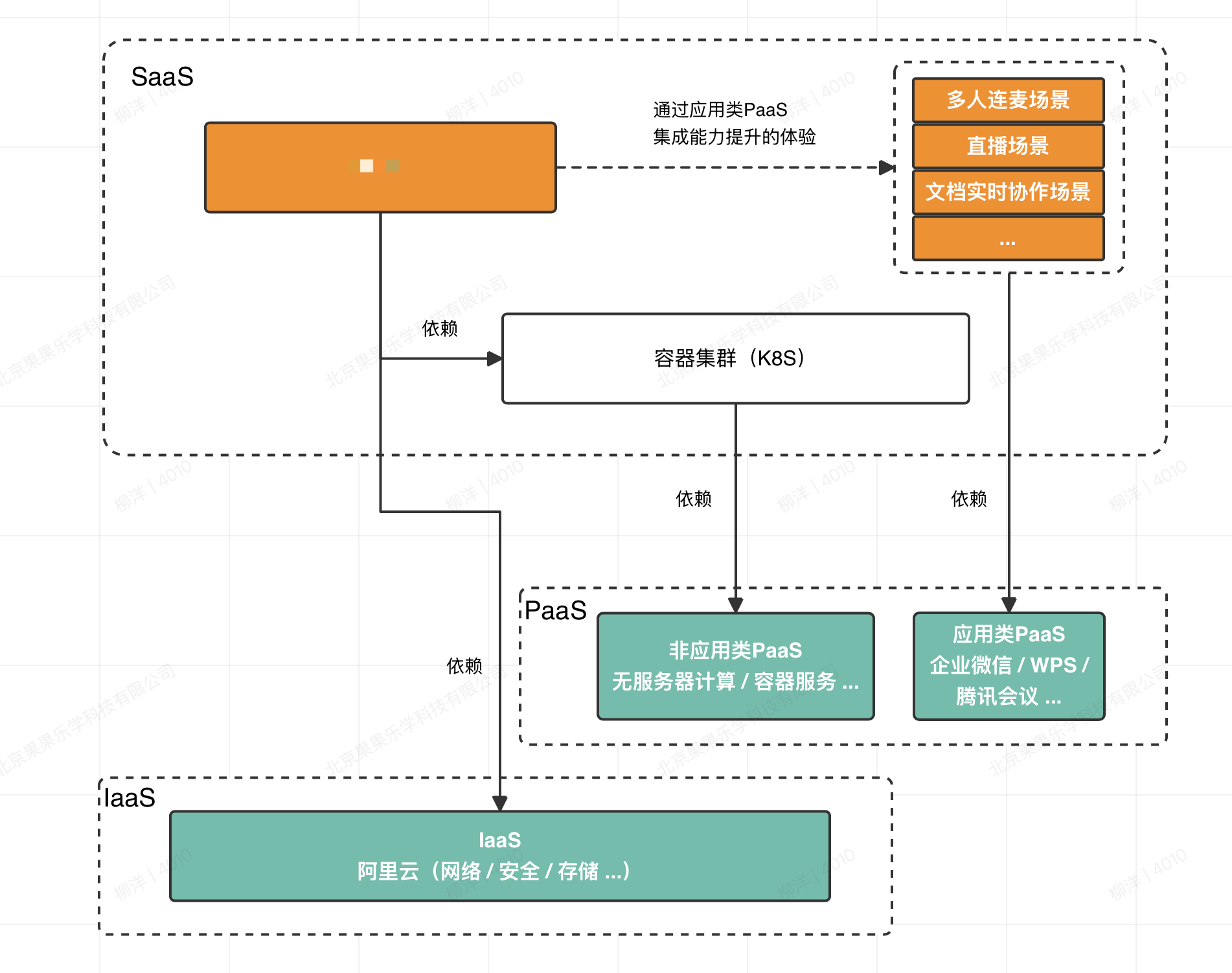
IaaS Layer
We primarily use Alibaba Cloud’s infrastructure for networking and storage to build our SaaS foundation.
PaaS Layer
Non-application Services
We mainly use Alibaba Cloud’s development platforms and environments to build and deploy application services, such as container services and serverless computing.
Application Services
- Video conferencing capabilities
- Document collaboration capabilities
- Live streaming capabilities
- AIGC
- …
SaaS Layer
We provide services to users through the SaaS layer.

- Cost efficiency: users do not need to buy expensive hardware or software licenses; they pay as needed
- Fast deployment: users can start by registering an account, reducing the time for traditional install and configuration
- Easy to scale: users can add or remove functional modules as needed
- Automatic updates and maintenance: the SaaS provider handles updates and maintenance, so users stay on the latest version without worrying about upgrades or security patches
- Convenient access: users can access SaaS services from any internet-connected device, supporting remote and mobile work and increasing flexibility
- Security: SaaS providers invest heavily in security such as encryption, backups, and disaster recovery, often more reliable than what small and medium businesses can manage themselves