Phase 1.0
Everything Starts from Requirements
During the 1.0 phase, we found many practical issues in implementation and usage. So we improved and upgraded the overall agile process to adapt to changes in team iterations.
Requirement Source Categories
Because requirement channels are diverse, we categorized sources for easier management:
| Requirement Code | Description | Iteration Version Code |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Product-value driven self-initiated iteration | feature/sprintXX, e.g. feature/sprint40 |
| CS | User-side requirements from Customer Success managers | cs/yyyyMMdd, e.g. cs/20210713 |
| Tech | Tech improvement or refactoring initiated by R&D | tech/module-or-refactor-name, e.g. tech/mtms, tech/res |
| Hotfix | Online issue fixes triggered by incident flow | hotfix/yyyyMMdd, e.g. hotfix/20210713 |
Currently, our team only triggers Sprints for feature requirements. Other types do not trigger Sprints.
Iteration Process
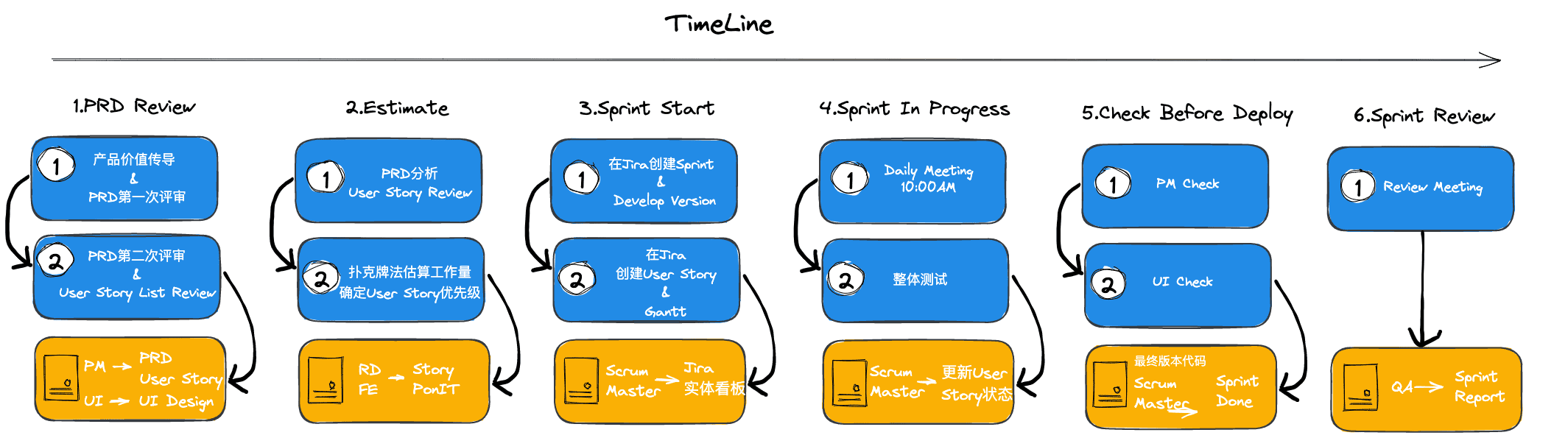
Overall, the iteration has 6 stages:
- PRD Review: Product requirement review, user story review
- Estimate: High-level design, effort estimation (planning poker)
- Sprint Start: Create Sprint in Jira, version number, register user stories, create Gantt
- Sprint In Progress: Iteration in progress, daily standup at 10am to sync
- Deploy: PM & UI acceptance, release
- Sprint Review: Iteration retrospective
1. PRD Review
PRD Review Flow
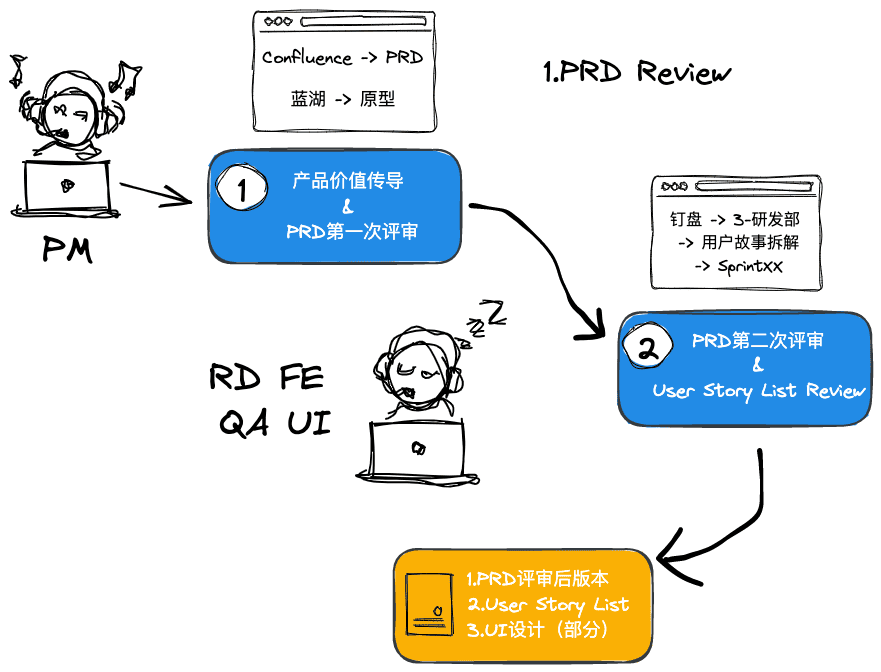
Participants
- Lead: PM
- Participants: RD FE QA UI
Input
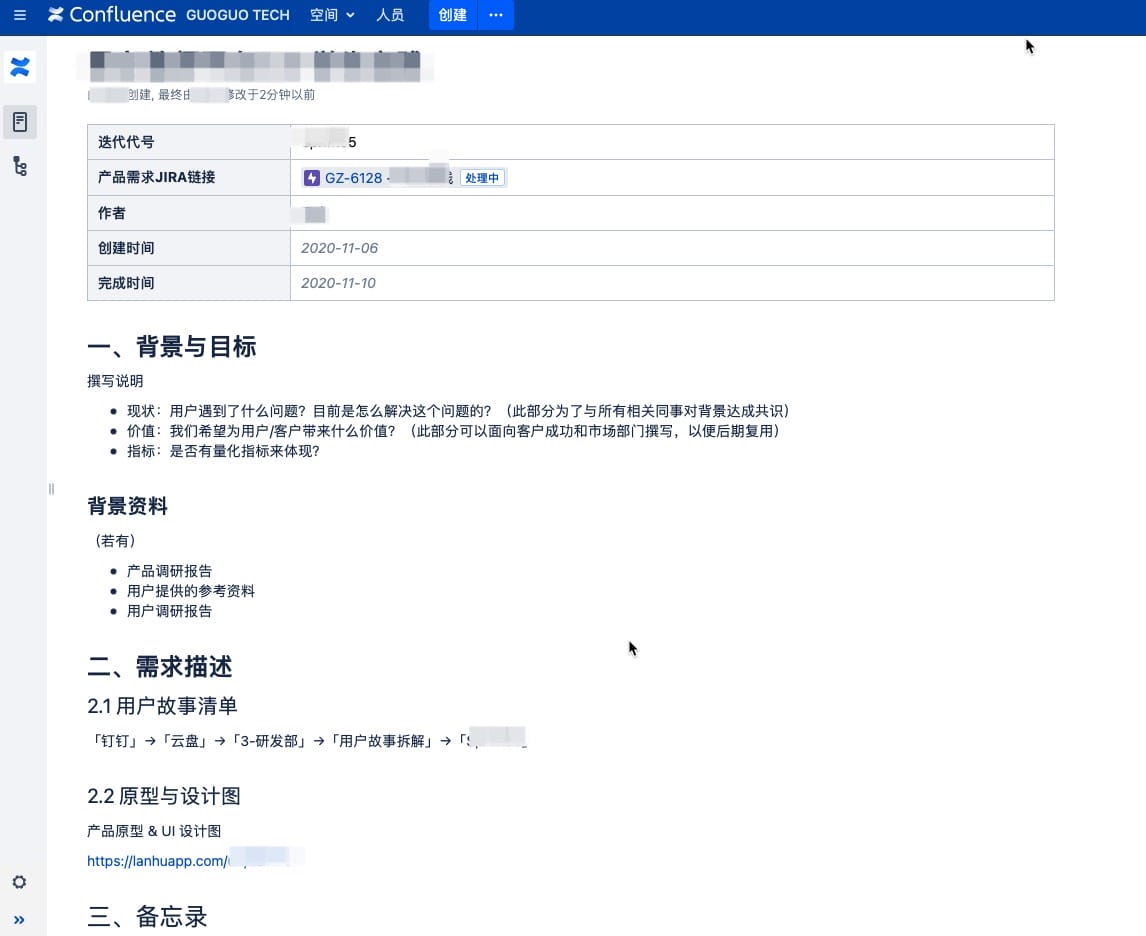
- PRD for this iteration. (Path: “PM Team” → “Product Requirements” → “2021 Product Requirements” → “Product Self-Iteration” → “PRD page of a specific iteration”)
Output
- Final prototype discussion in Lanhu
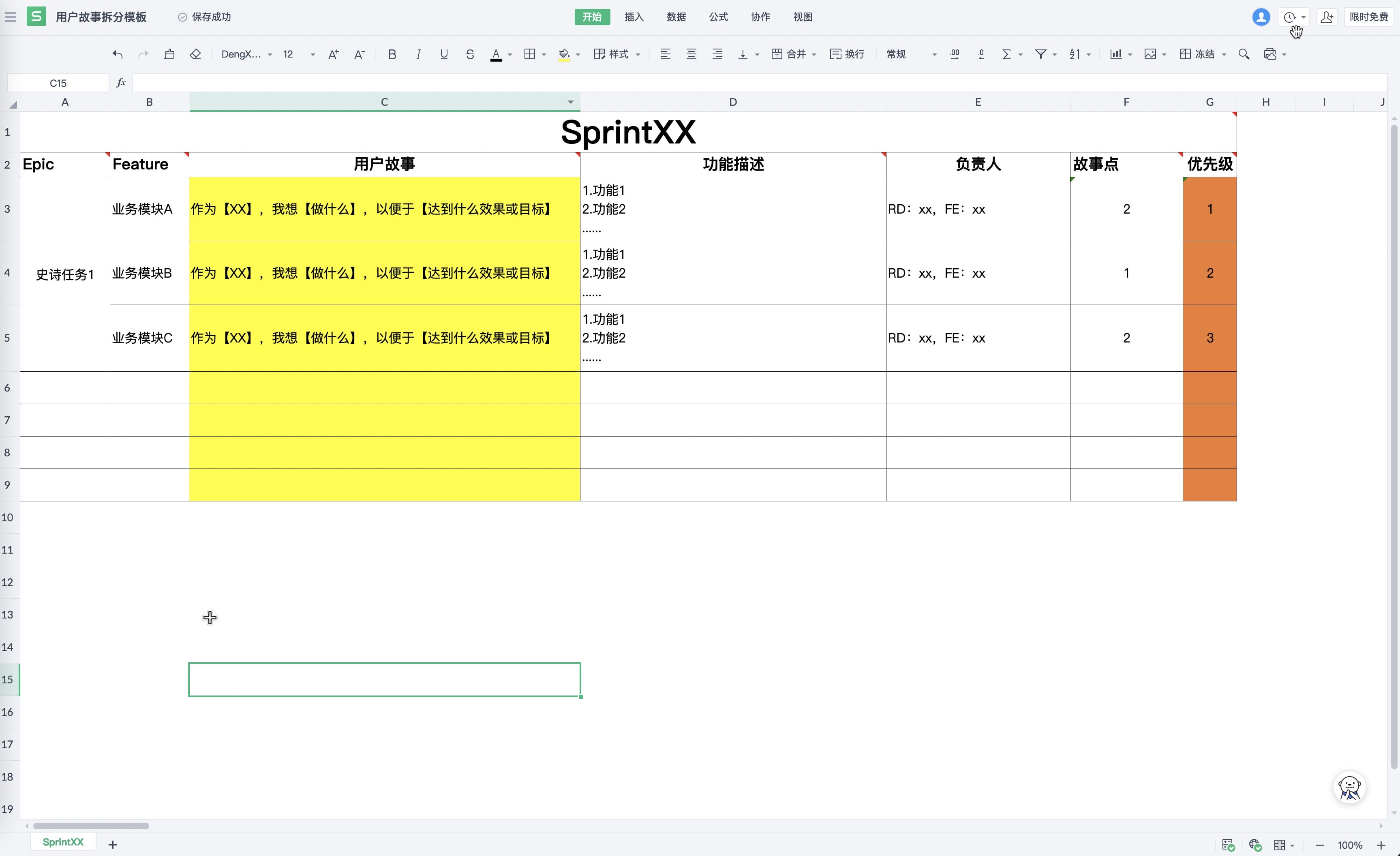
- Final user story discussion (Path: “DingTalk Drive” → “3-R&D Dept” → “User Story Breakdown” → “SprintXX” → “User story files in the folder”)
PRD
User stories in DingTalk
2. Estimate
We use Planning Poker. It’s a consensus-based estimation method (a game) used to estimate development effort in Scrum iterations. Through team consensus, deviation becomes relatively small.
What Is Planning Poker
Planning Poker uses the Fibonacci sequence as Story Points. The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers introduced in the 13th century, used to explain patterns in nature (e.g., tree branching). The next value is the sum of the previous two: 0, 1/2, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20. For agile estimation, some numbers are adjusted to: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40, 100.
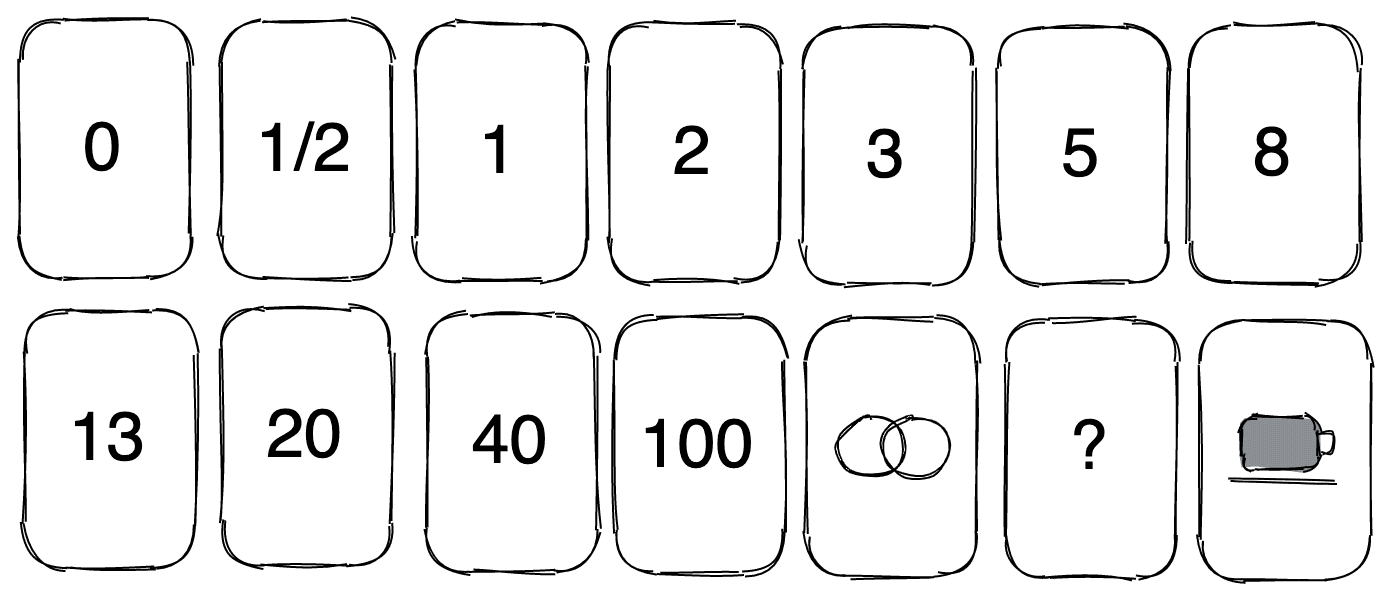
Poker legend (point convention: 1 Story Point = 1 person/day)
| Card | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 0 | No work needed |
| Infinity | Large task |
| ? | Cannot estimate |
| A cup of coffee | Less than 0.5 |
| Others | Interpret points literally |
Estimation Flow
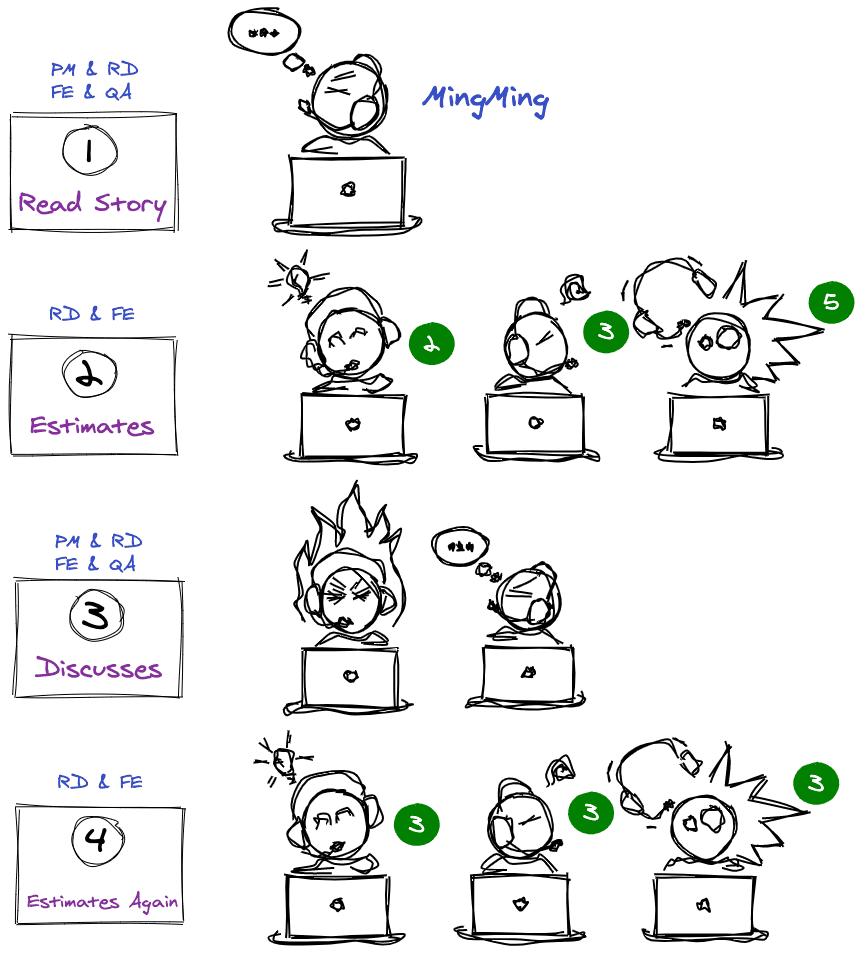
Participants
- Lead: PM
- Participants: RD FE QA
Input
- User stories
Output
- Estimates and priorities for user stories
Steps (usually consensus is reached within 2 rounds)
- PM describes the user story
- RD / FE team members play cards face down (Fibonacci values: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40)
- Reveal cards simultaneously
- Explain estimation differences and discuss
- Reach estimation consensus
Estimation record
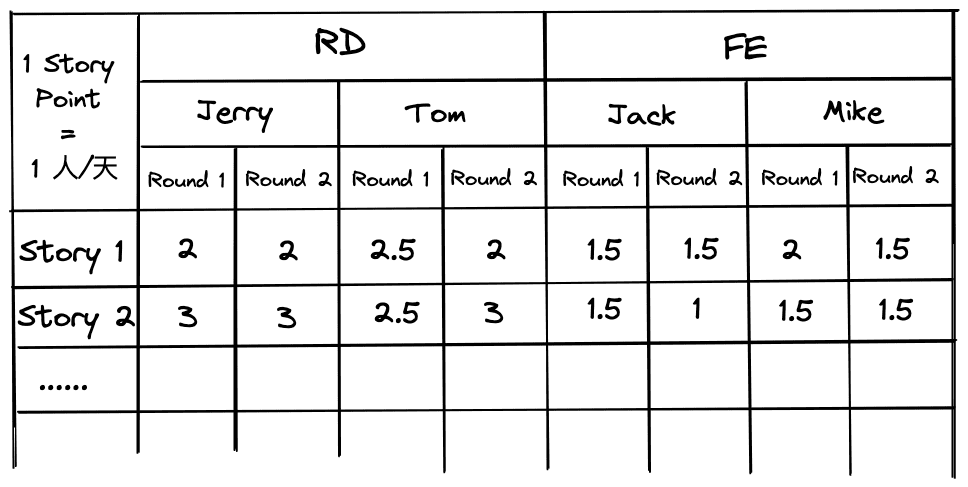
After estimation, we fill the results into the story list in DingTalk Drive and confirm story priorities.
3. Sprint Start
Sprint Creation & Start Flow
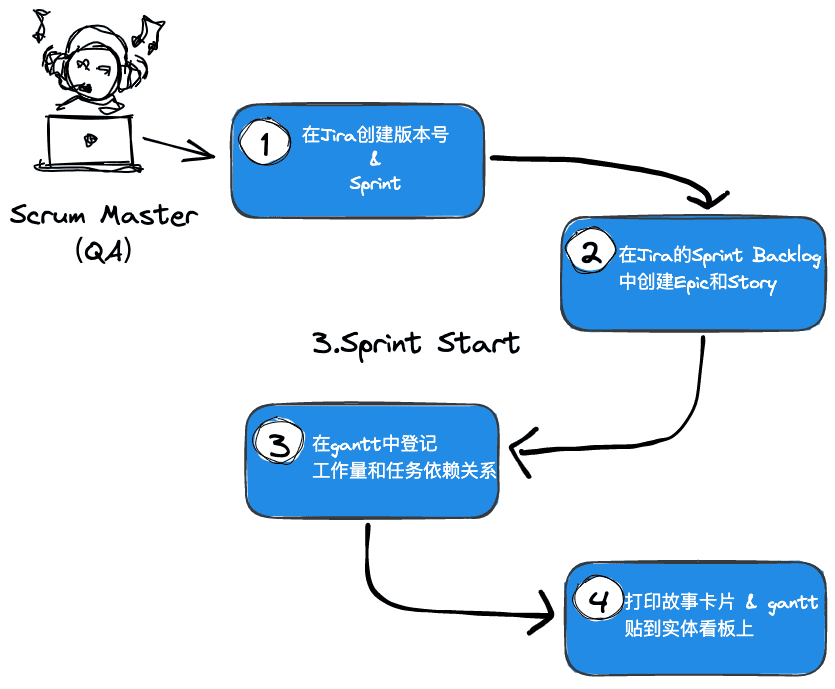
Participants
- Lead: Scrum Master (QA)
- Participants: RD FE QA
Input
- User stories & estimation results
Output
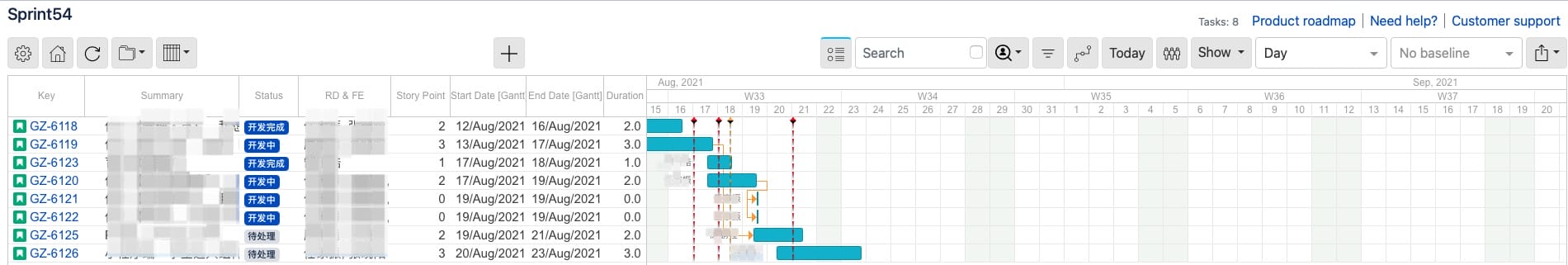
- Sprint & Gantt
Create Epic
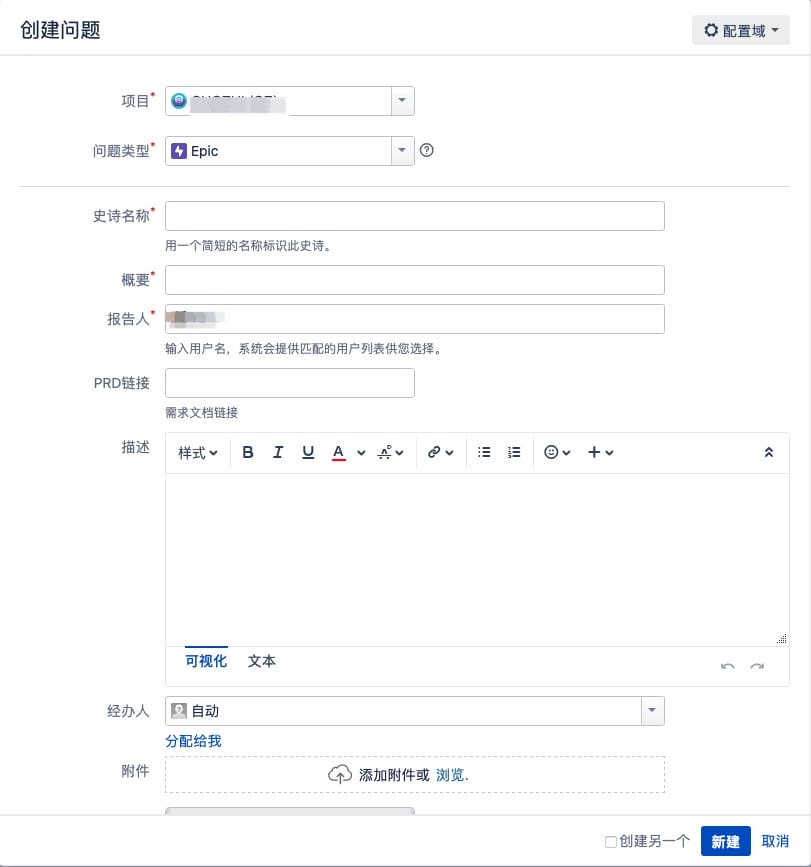
Create Story
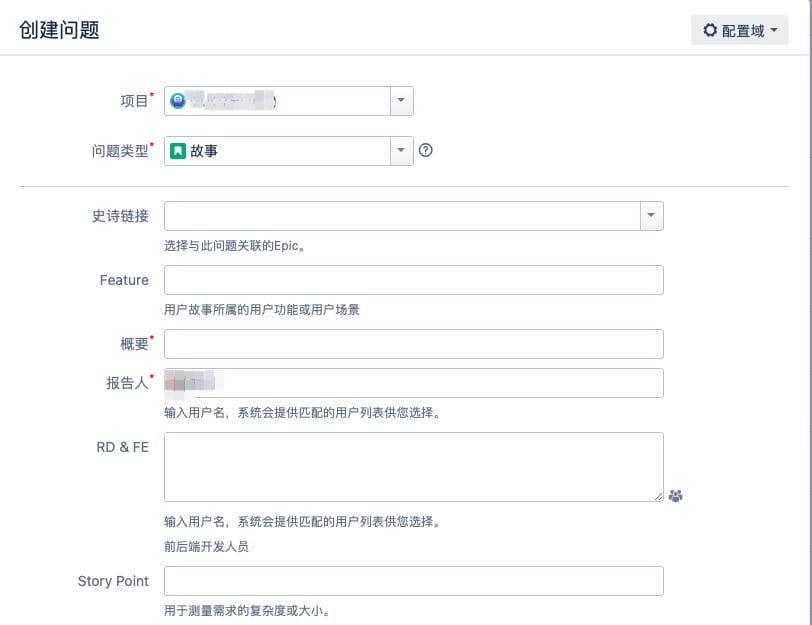
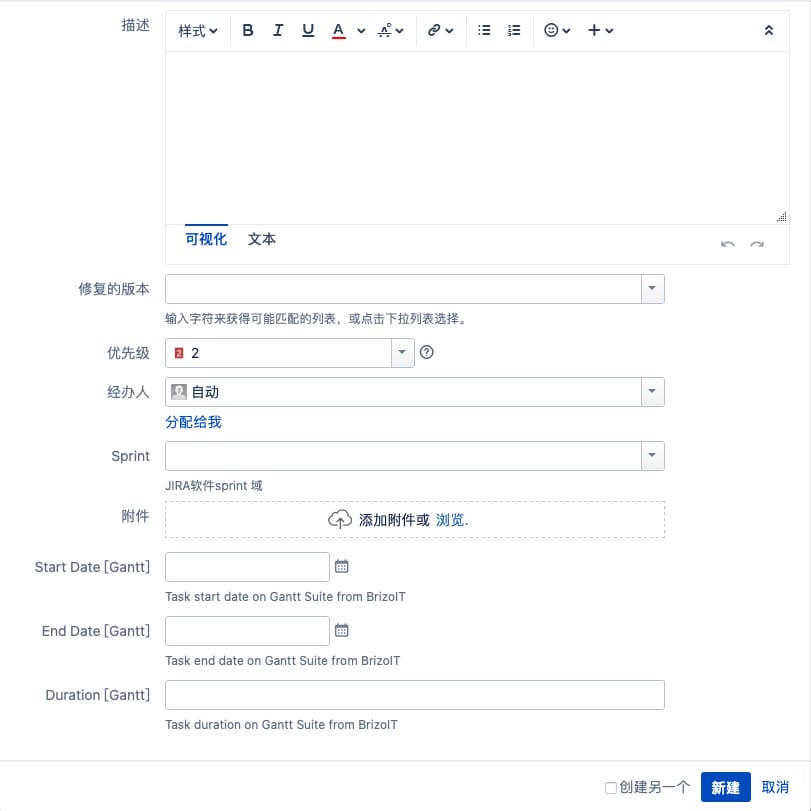
\
Sprint board
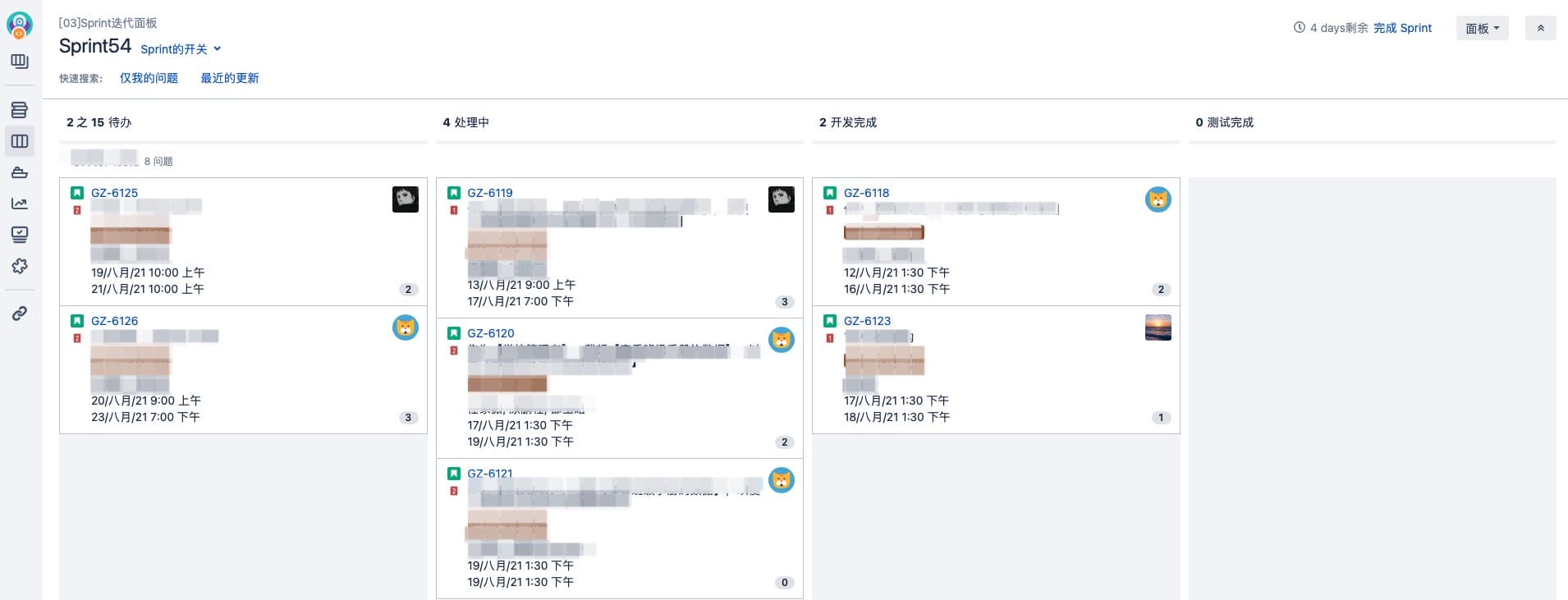
Gantt
4. Sprint In Progress
Daily Flow
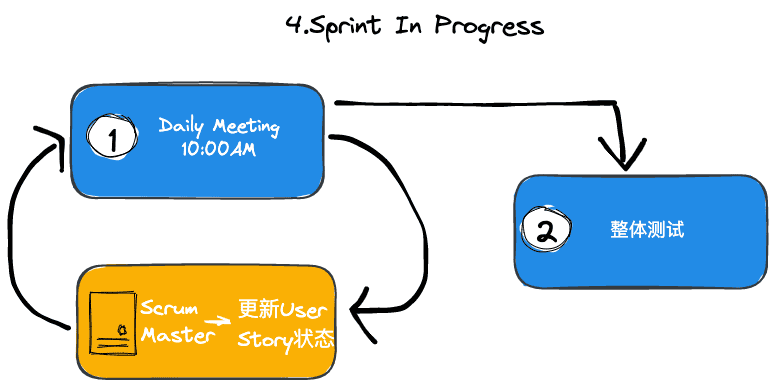
Participants
- Lead: Scrum Master (QA)
- Participants: RD FE QA
Input
- Standup sync
Output
- User story updates
5. Deploy
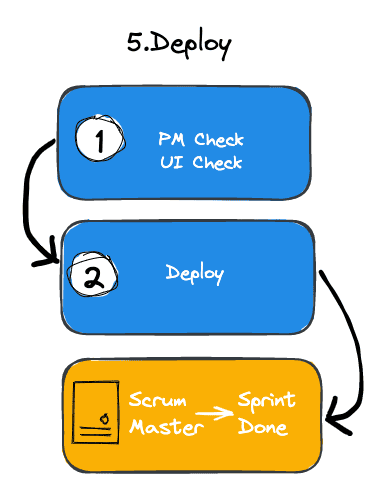
Acceptance & Release Flow
Participants
- Lead: Scrum Master (QA)
- Participants: PM UI RD FE
Input
- UAT environment
Output
- Iteration release
- Sprint Done
6. Sprint Review
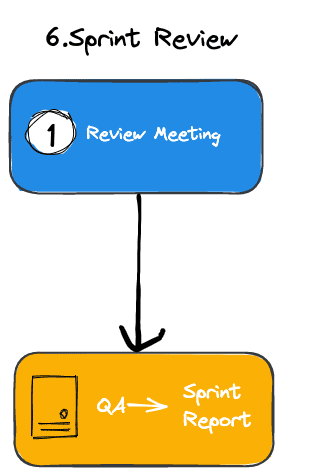
Review Flow
Participants
- Lead: QA
- Participants: PM UI RD FE
Input
- Test report
Output
- Retrospective results
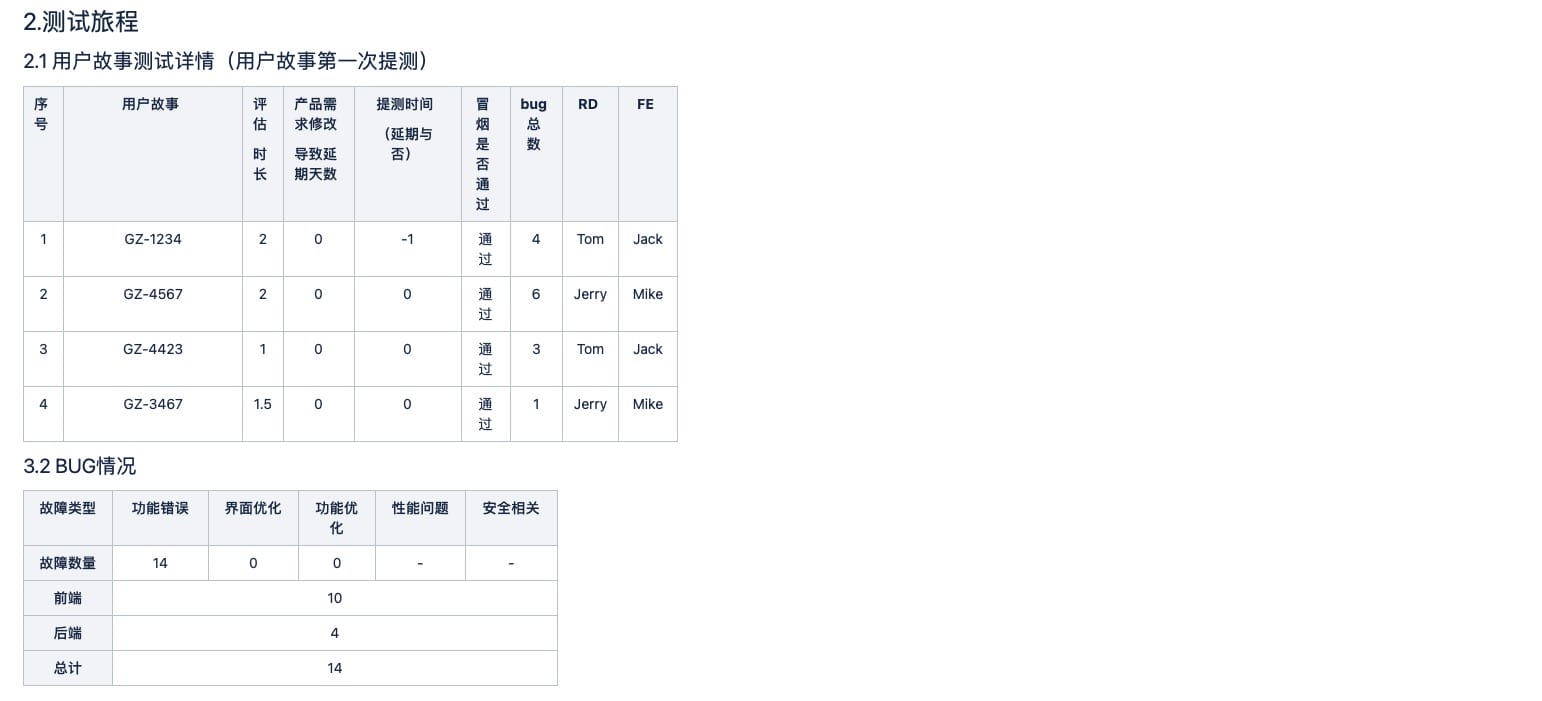
Test report


Summary
The above is the current 2.0 version of our R&D team’s agile iteration process. The key improvements ahead are introducing CI, automated testing, and other approaches to further improve testing efficiency and surface issues faster.