Preface
Iteration management looks different at every company. As product stages, team size, and resources change, the process evolves through practice and optimization. In my team, we review our iteration process every six months and make adjustments.
Below is the iteration workflow we optimized in early 2023.
What Problems Iteration Management Solves
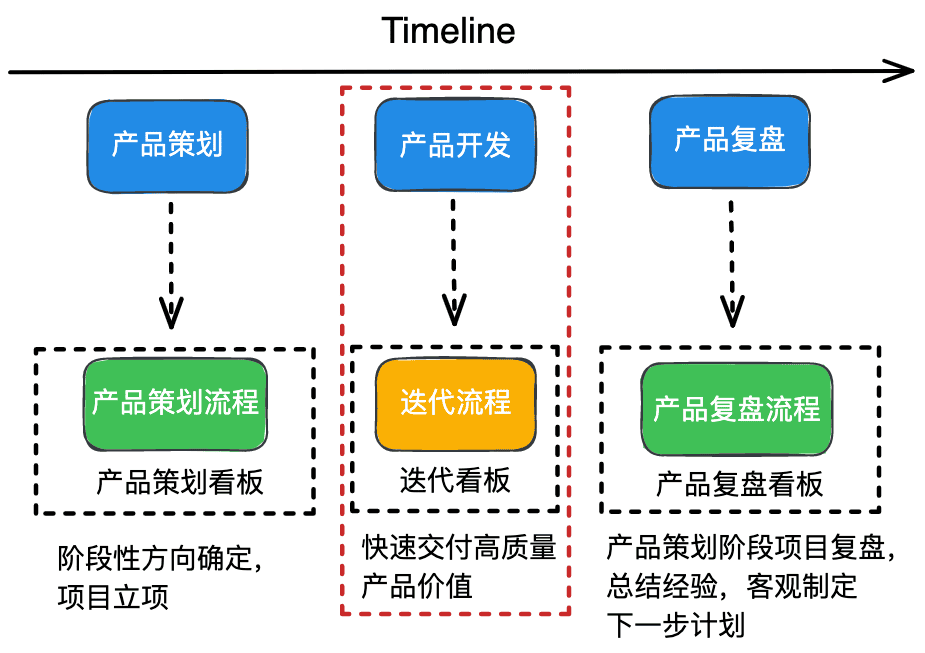
In the diagram above there are three phases. The “product development” phase is the iteration process described below.
Development Process Methodology
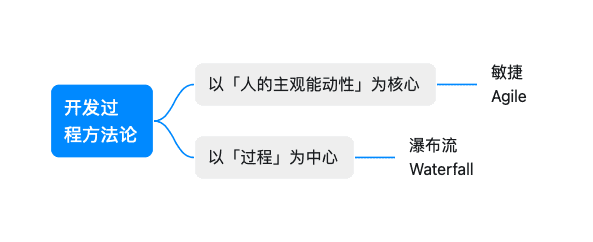
Principles and Framework
Note: For the overall iteration cycle, we split it into larger stages that resemble a “waterfall” approach.
For requirement understanding and delivery, we use an agile approach and deliver/accept at the story level.
Principles We Follow
People’s initiative at the core: deliver higher-value products efficiently and with quality, and help team members become the best version of themselves.
Framework We Use
Scrum + Kanban
The goal of Agile is to help us discover how bad things are as early as possible, and start managing the situation early.
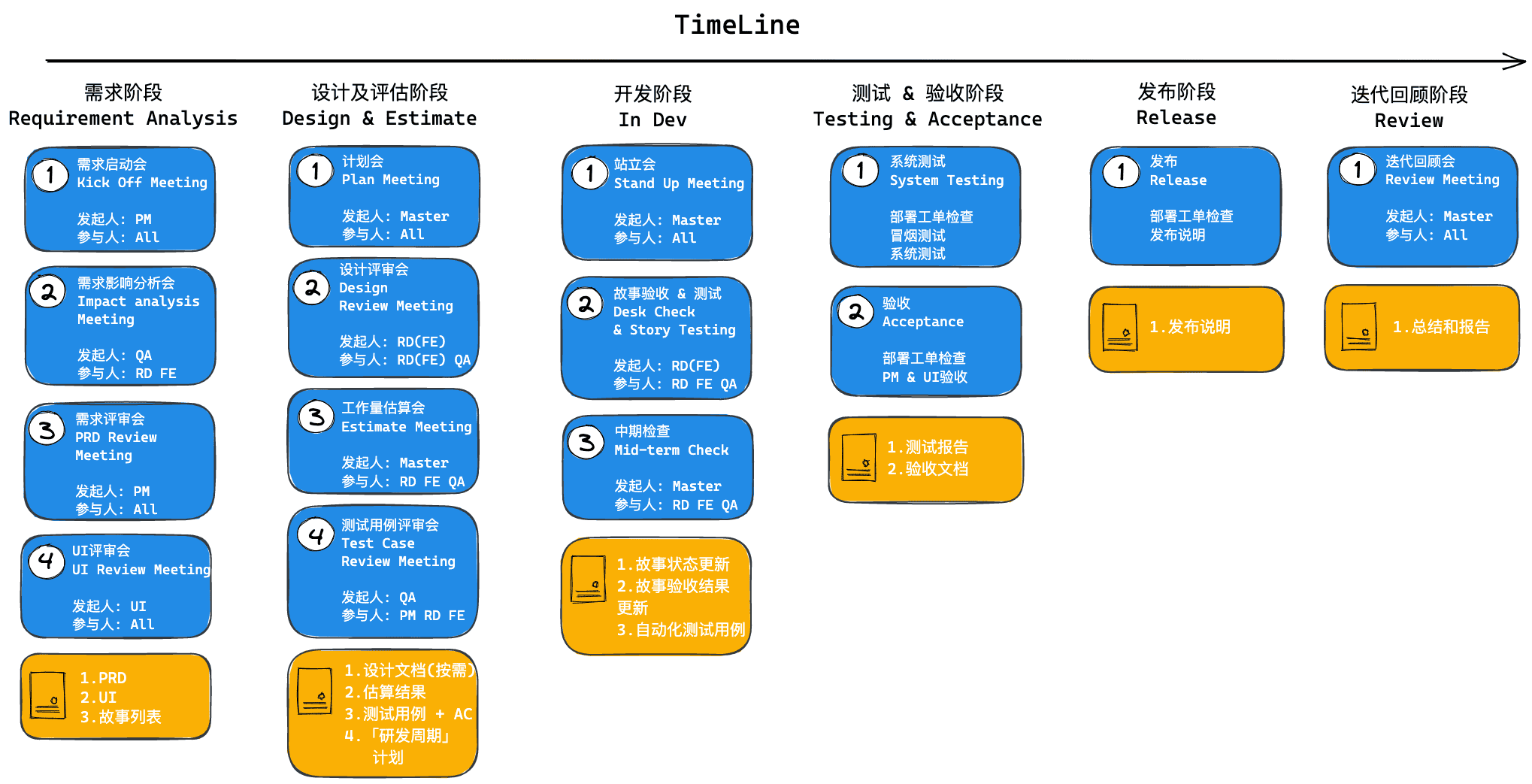
Process Overview
Roles
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Scrum Master | Agile coach, drives iterations; currently handled by QA |
| PM | Product manager, produces and explains the PRD |
| RD | Backend engineer, responsible for backend implementation |
| FE | Frontend engineer, responsible for frontend implementation |
| QA | Test engineer, responsible for iteration quality |
| UI | UI designer, responsible for interaction and visual design |
Detailed Breakdown
Requirements Phase
Kick Off Meeting
Goal: A kickoff, as the name suggests. Communicate product value, why we are doing it, and the iteration goals. No deep dive into product or prototype details.
Participants: Everyone
Actions
- PM -> present the product value in the PRD
- Master -> create the iteration version in the project management platform
- Master -> create a communication group in the communication tool
Impact Analysis Meeting
Goal: Understand existing system functionality and analyze the impact of this iteration
Participants: RD, FE, QA
Actions
- RD or FE -> explain current system features and analyze impact
PRD Review Meeting
Goal: Discuss requirements, implementation logic, and rule details to reach team-wide alignment on understanding (typically no more than 2 meetings).
Participants: Everyone
Actions
- PM -> deliver the final PRD
UI Review Meeting
Goal: Discuss page and interaction implementation to reach a shared understanding of UI/UX (typically no more than 2 meetings).
Participants: Everyone
Actions
- UI -> deliver page and interaction designs
Design and Estimation Phase
Plan Meeting
Goal: Confirm iteration scope, including business work, technical work, and backlog or bugs.
Participants: Everyone
Actions
- Master -> organize the plan meeting and confirm scope (review backlog and bugs in the project management platform)
Design Review Meeting
Goal: Discuss design, standards, implementation, data migration, historical tech debt, and release plans.
Participants: RD or FE, QA
Actions
- (As needed) RD -> produce design doc and review it (see How to write a design doc TODO)
- First review: RD internal design review
- Second review: RD + FE API design review
- (As needed) FE -> produce design doc and review it
Estimate Meeting
Goal: Based on the confirmed scope from the plan meeting, estimate effort and assign priorities and owners.
Participants: RD, FE, QA
Actions
- Master -> organize the estimate meeting and confirm effort (estimation method: planning poker TODO)
“R&D Cycle” Plan Release
Actions
- QA -> publish the iteration “R&D cycle” plan
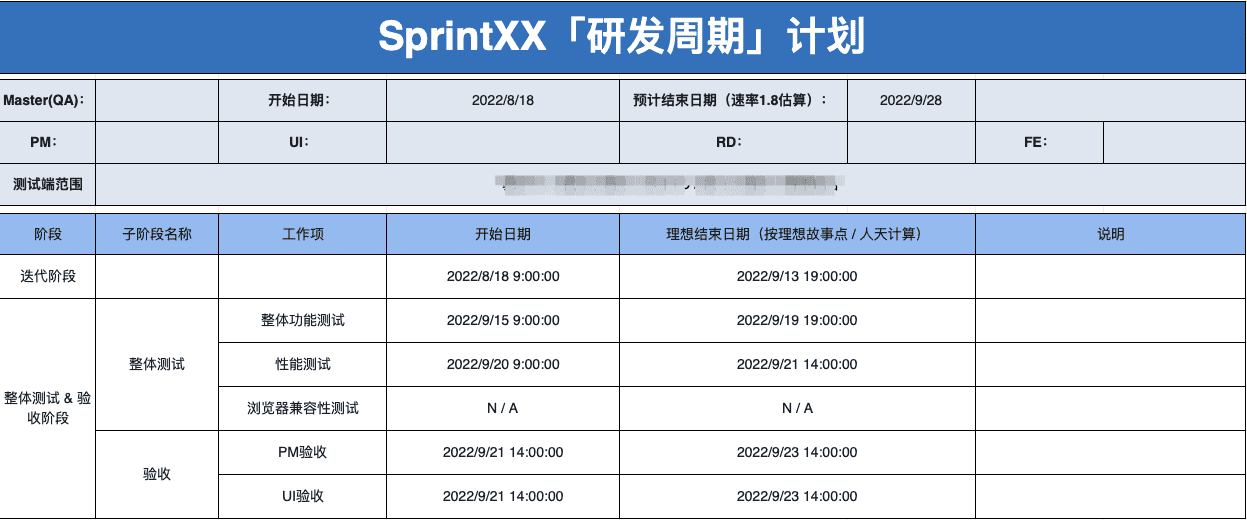
- Master -> update all iteration info in the project management platform and officially enter coding
Test Case Review Meeting
Goal: Review completeness and quality of test cases.
Participants: RD, FE, QA
Actions
- QA -> organize the review (test cases maintained in the test case management platform)
Development Phase
Daily Stand-up Meeting
Goal: See TODO: How to run daily stand-ups
Participants: Everyone
Actions
- Master -> run the meeting, focusing on dependencies, blockers, risks, etc.
Desk Check and Story Testing
Actions
- RD & FE -> initiate story acceptance (how to do story acceptance TODO). After it passes, deploy to FAT for testing; QA records results.
- QA -> test the story; if there are no functional issues, close the story testing
Mid-term Check
Goal: Surface issues and anticipate risks
Actions
- Master -> at the midpoint of the iteration, organize a progress review to detect delay risks
Test and Acceptance Phase
System Testing
Actions
- RD & FE -> prepare deployment docs and submit deployment tickets
- QA -> in FAT
- validate deployment docs
- smoke testing
- test cases (black-box, white-box)
- regression testing (black-box, white-box)
Acceptance
Actions
- QA -> in UAT
- validate deployment docs
- PM -> product acceptance
- UI -> UI acceptance
- QA -> in UAT
- regression testing (black-box, white-box)
Release Phase
Release
Actions
- QA -> submit deployment ticket for approval, then release
- QA -> fill out release notes (internal)
Iteration Retrospective Phase
Review Meeting
Goal: Summarize iteration process and quality issues, run a retrospective, and optimize process, code quality, and collaboration.
Participants: Everyone
Actions
- Master -> gather iteration data and write the report
- Master -> organize a full-team review and discussion
Tools and Platforms
| Tool or Platform | |
|---|---|
| Project management platform | https://www.teambition.com/ |
| Communication tool | DingTalk |
| Test case management platform | https://metersphere.io |