What Is Planning Poker
A consensus-based estimation method (a game) used to estimate effort for Scrum iteration tasks. By evaluating together as a team, the variance becomes smaller.
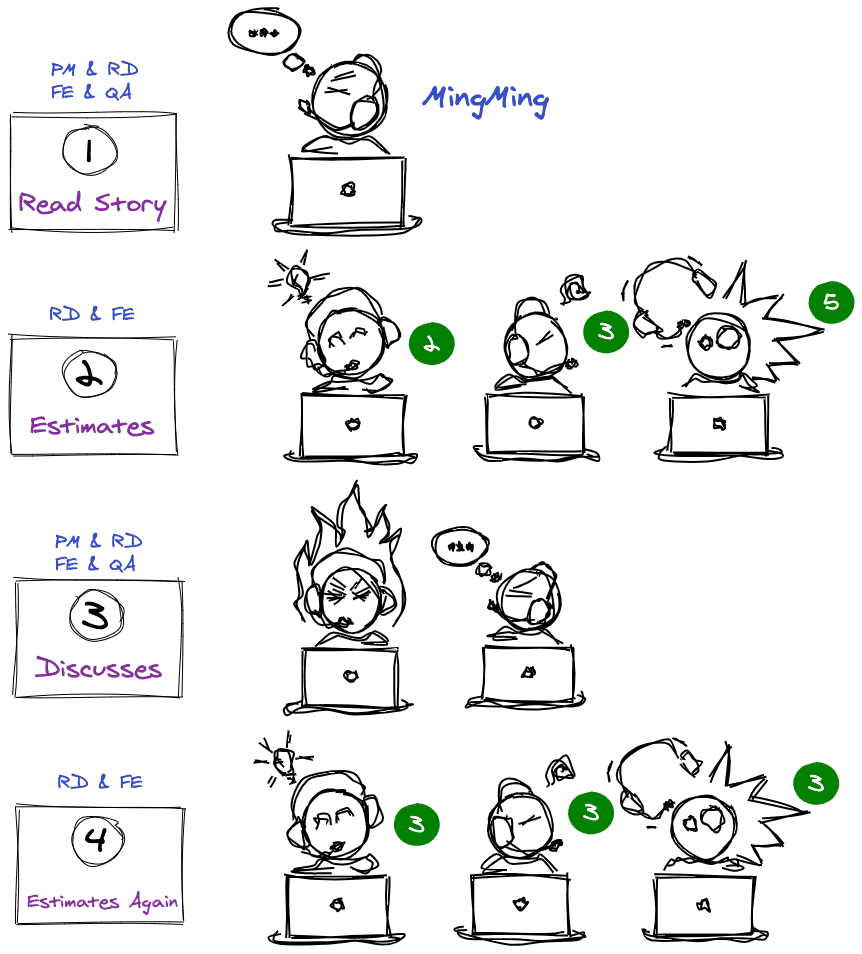
Implementation Steps
Roles
| Participant | Description |
|---|---|
| Scrum Master (QA) | Facilitates the estimation process |
| PM | Explains and describes the stories |
| RD / FE | Developers who estimate |
| RD TL / FE TL | Judges the reasonableness of story points |
Round 1
-
- PM explains the story
-
- RD / FE place numbered cards face down; Scrum Master calls reveal and everyone flips at once (Fibonacci values: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40)
-
- Explain estimation differences and discuss
-
- Reach consensus
Round 2
-
- For stories with differing points, RD / FE explain their estimation differences and reach consensus
-
- Scrum Master writes the final story points into the story list
-
- Everyone ranks priorities and fills them into the story list
Fibonacci Sequence and Planning Poker
Planning poker uses the Fibonacci sequence as story points. The Fibonacci sequence is a numeric series introduced in the 13th century that explains certain formations in nature, like branching in trees. Each next value is the sum of the previous two: 0, 1/2, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, etc.
For agile estimation, some values are adjusted, resulting in the following series: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40, 100, as shown below:

Point convention: 1 Story Point ~= 1 person-day in ideal conditions (based on average team capability).
| Card | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | No effort needed |
| ? | Cannot estimate |
| Others | Interpret the number as the point value |